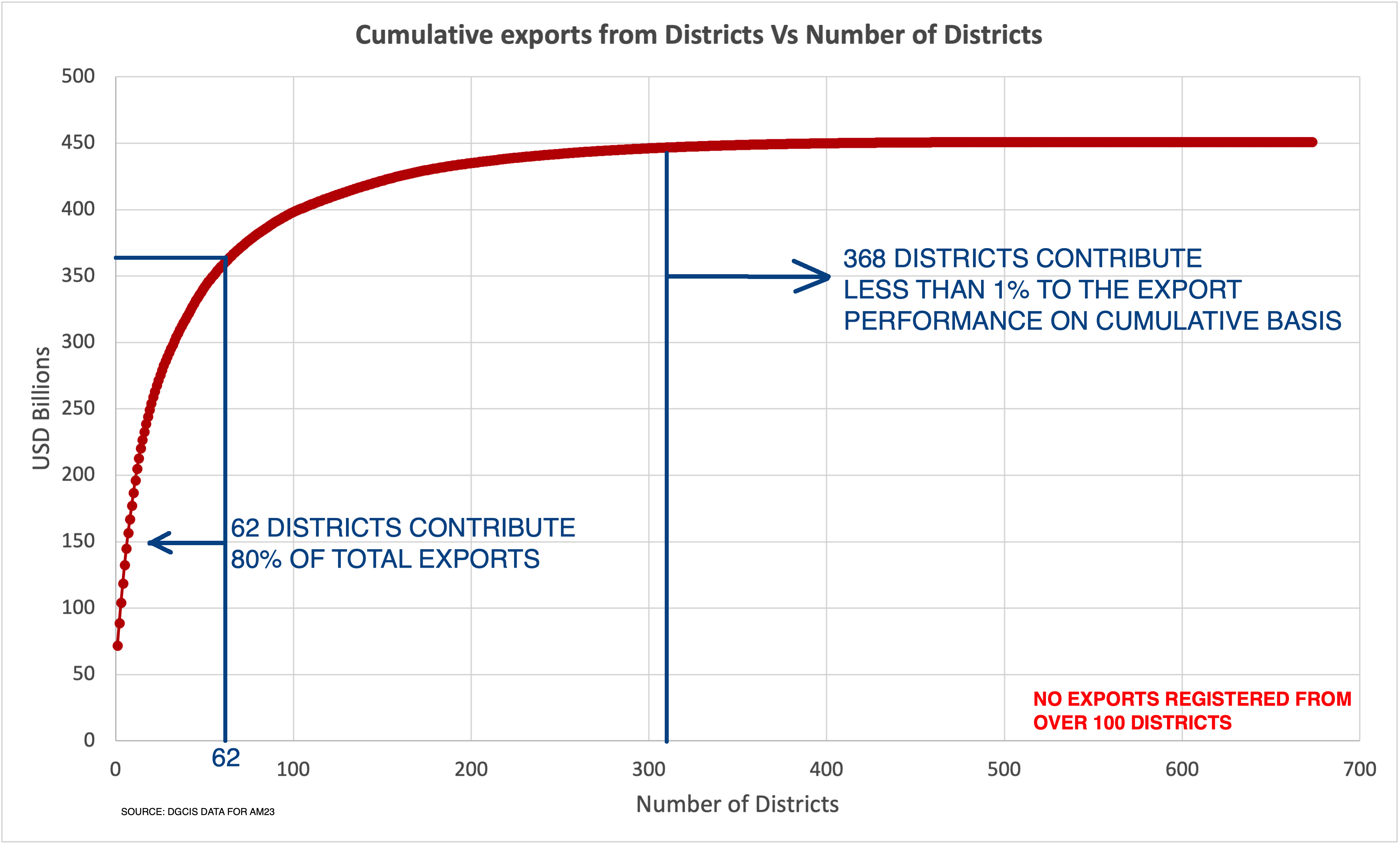
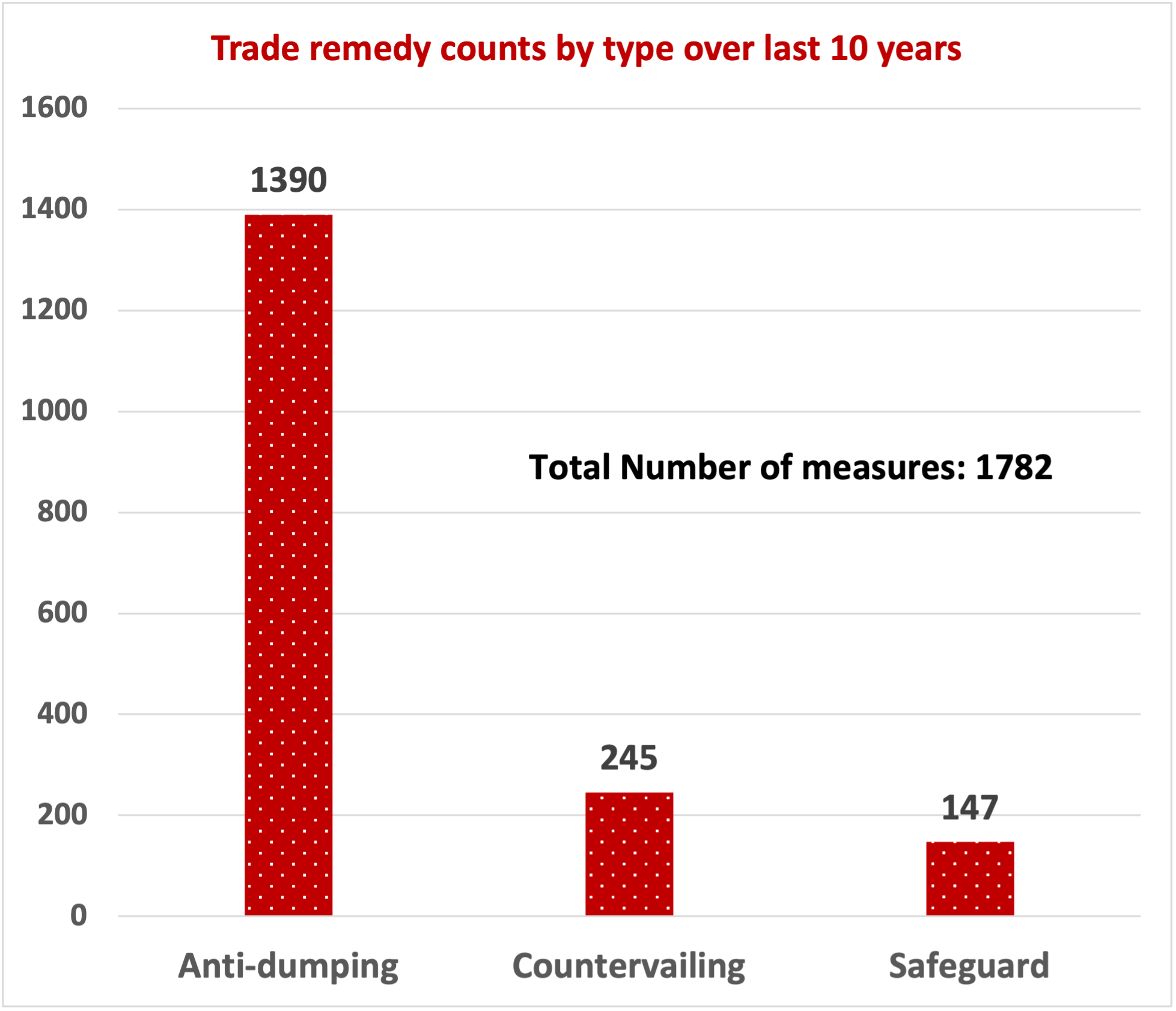
E-Commerce exports from India: The engine for USD 1 trillion goods exports by 2030 – Part 2
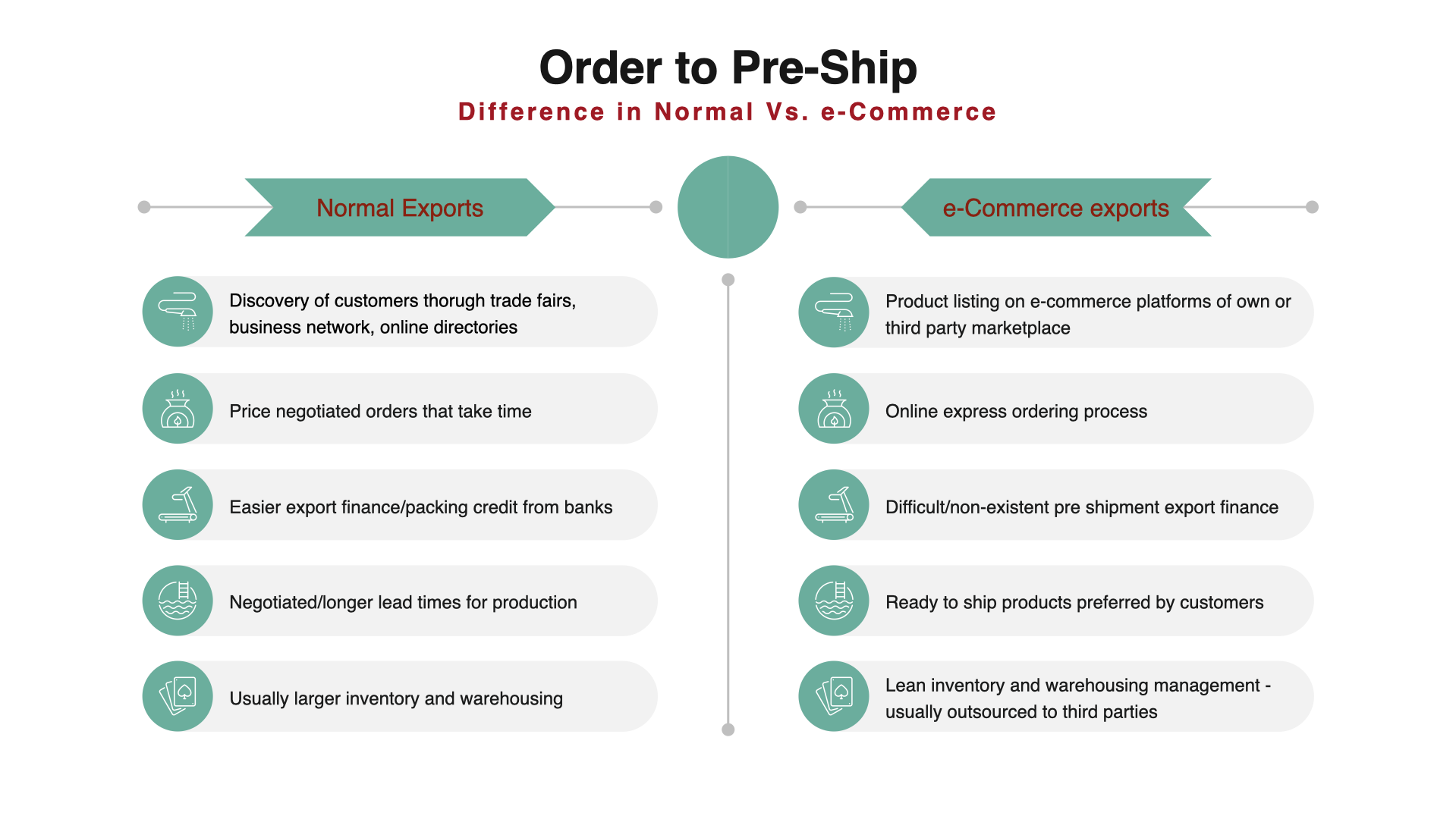
This is the second part in the two part series where we are looking at the e-commerce exports from India. The first part had set the context, and the second part now delves into the policy and regulatory aspects. The post was originally published here: https://swarajyamag.com/business/e-commerce-exports-unlocking-the-potential-of-indias-msme-sector-in-international-trade Imagine a rural artisan in India effortlessly connecting with an international customer, focusing solely on perfecting her craft while the system handles everything from product listing to payment settlement. This is the transformative potential of e-commerce exports, empowering MSMEs and entrepreneurs to participate in the global marketplace, aligning with the Prime Minister's vision of "Vocal for Local, Local for Global." However, realizing this vision requires a robust framework that addresses the unique challenges and opportunities of digital trade. In this second part, we explore the key eleme